NeurOs
The Most Accurate, Cost Effective, and User Friendly Cerebral Tissue Oximetry System
- High absolute trending accuracy ± 1.5% of tissue oxygenation
- New Index of Blood Volume Fraction for monitoring tissue vascular filling
- Reusable sensors with the best signal quality at a fraction of the cost compared to the existing one time use sensors
- Operates on either tablet, laptop, computer, or any third-party monitors of the customers choice
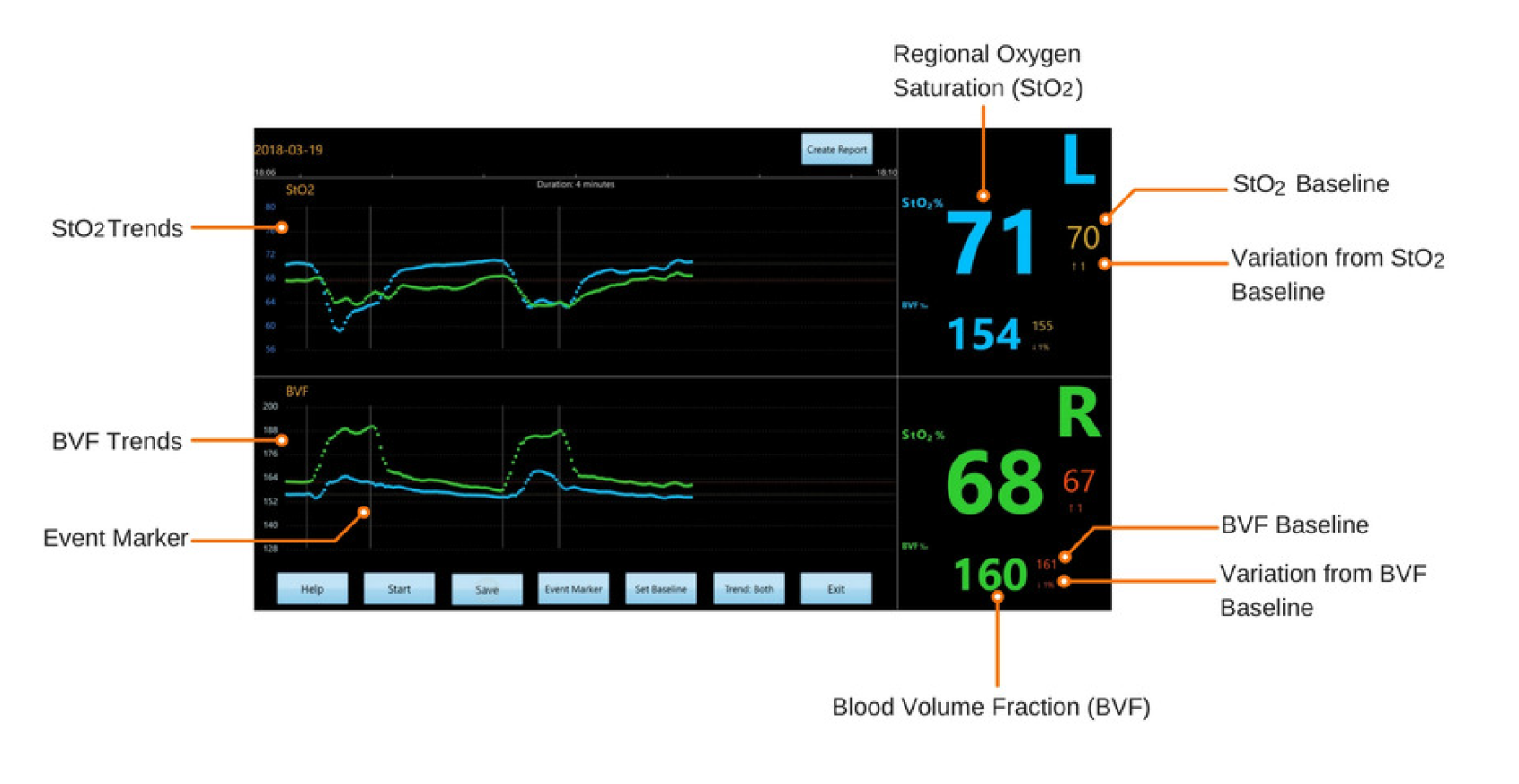
NeurOs Display |
NeurOs Sensor |


For a PDF version, please download this document.
Clinical Validation of Mespere NeurOs against Invasive Blood Sample Analysis By Co-Oximeter
Methods |
A peripheral IV was placed in the patient’s hand or arm vein. An ultrasound-guided small diameter catheter was then inserted in the right upper internal jugular vein. A radial arterial line was inserted into a radial artery on the left arm. Two standard pulse oximeters were attached to the patient’s fingers to help guide the hypoxia state plateau levels. The Mespere Cerebral Oximetry sensor was placed on the forehead. Blood gas analysis to determine oxyhemoglobin saturation was performed using a Co-Oximeter. Each subject had control data taken at the beginning of each experiment, with two control blood samples drawn while breathing room air. Hypoxia was induced to different levels of oxyhemoglobin saturation (between 70-100% SpO2) by having subjects breathe mixtures of nitrogen, room air, and carbon dioxide. Once a steady state level of hypoxia is achieved, a 1.0ml sample of blood are obtained simultaneously from the jugular line and radial arterial line. A second blood pair of samples, at the same steady-state saturation, is taken 30 seconds later. The VO200 - NeurOs Cerebral Oximetry samples were recorded simultaneously to the blood samples. The blood samples were immediately analyzed by the Co-Oximeter. Up to 27 paired samples were obtained on the plateaus across this span for each subject.
Results |
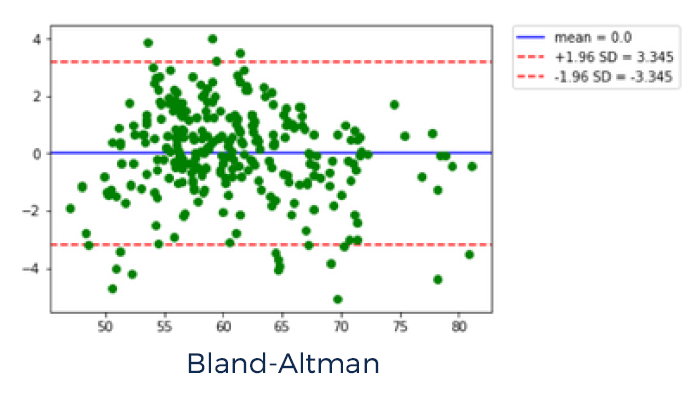
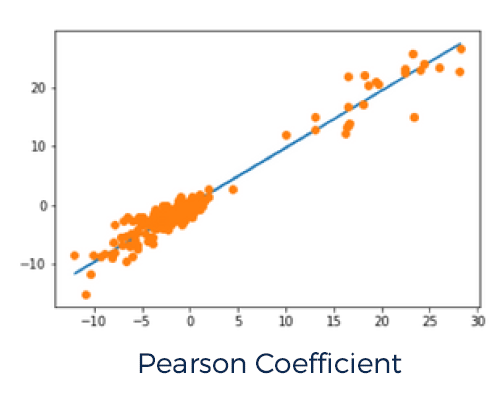
A total of 284 paired venous and arterial blood sample readings, and 284 Mespere VO 200- NeurOs Cerebral Oximetry System readings were used to perform the comparison and statistical analysis.
The calculated statistical results from the study are as follows:
| Absolute Trending Accuracy | ± 1.5% |
| Pearson Coefficient | 0.973 |
For a PDF version, please download this
document.

Scenario
| Number of Cases Per Year: | 500 |
| Cost of ICU Stay Per Day: | $3592 |
| Cost of Non-ICU Stay Per Day: | $1135 |
Mespere vs. Competitors Sensor Savings
| COMPETITOR | MESPERE | |
| Comparison cost per patient: | $300 | $50 |
| Total cost per year: | $150,000 | $25,000 |
Net Savings by Mespere: $125,000
Hospital Savings
| SAVINGS | TOTAL |
| Number of Cases per year: | 500 |
| Number of Cases at risk of cerebral desaturation (20%): | 100 |
| Decrease in ICU days using Cerebral Oximeter per patient: | 3 |
| Total Decrease in ICU days using Cerebral Oximeter per year: | 300 |
| Cost of ICU stay per day: | $3,592 |
| Total Savings - ICU Stay: | $1,077,600 |
| Decrease in Non- ICU days using Cerebral Oximeter per patient: | 1 |
| Total Decrease in ICU days using Cerebral Oximeter per year: | 100 |
| Cost of Non-ICU stay per day: | $1,350 |
| Total Savings - ICU Stay: | $135,000 |
| Cost of Mespere sensors per patient: | $50 |
| Cost per year | $25,000 |
Net Savings to hospital: $1,187,600
For a PDF version, please download this
document.


